Gas Chromatography GC Analysis
Gas Chromatography GC is technique which is suited to the analysis of small, relatively volatile molecules. It can be used both to identify and quantify substances. In general for measurements a sample or solution of the pure material and these are often obtained from specialist suppliers.
Most samples have to be prepared and LPD Lab Services has a wide variety of extractive techniques which are available to our experienced analytical staff . While some chemicals are relatively non-volatile they can be reacted by the laboratory to form derivatives which can then be analysed by GC.
One of the problems which can be encountered is the analysis of residual solvents in solid samples. This problem can be resolved by the use of a headspace sampler which is used to extract the analyte from the sample and introduce it into the GC.
Detection on our system is achieved by use of a flame ionisation detector FID which is effective down to low levels, typically 1 to 20 micrograms in a gram of sample (ppm) although this is dependent upon the extraction techniques employed. If greater sensitivity is needed we can then use Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry GC-MS which is up to 1000 times more sensitive.
The laboratory also has a GC-MS capability for more detailed breakdown of unknown or mixed organic chemicals or materials.
 Typical Applications of GC
Typical Applications of GC
- Analysis of organic chemical mixtures.
- Alcohol content measurements in hand sanitiser gel formulations like IPA and ethanol.
- Trace analysis of organic species.
- Waste solvent quantification.
- Health and Safety monitoring of organic species.
- Measurement of volatile species like waste solvent mixtures.
- Deformulation and quantification of organic species.
- Atmospheric sampling.
- Electronic Cigarette nicotine determinations.
Principles of Gas Chromatography GC
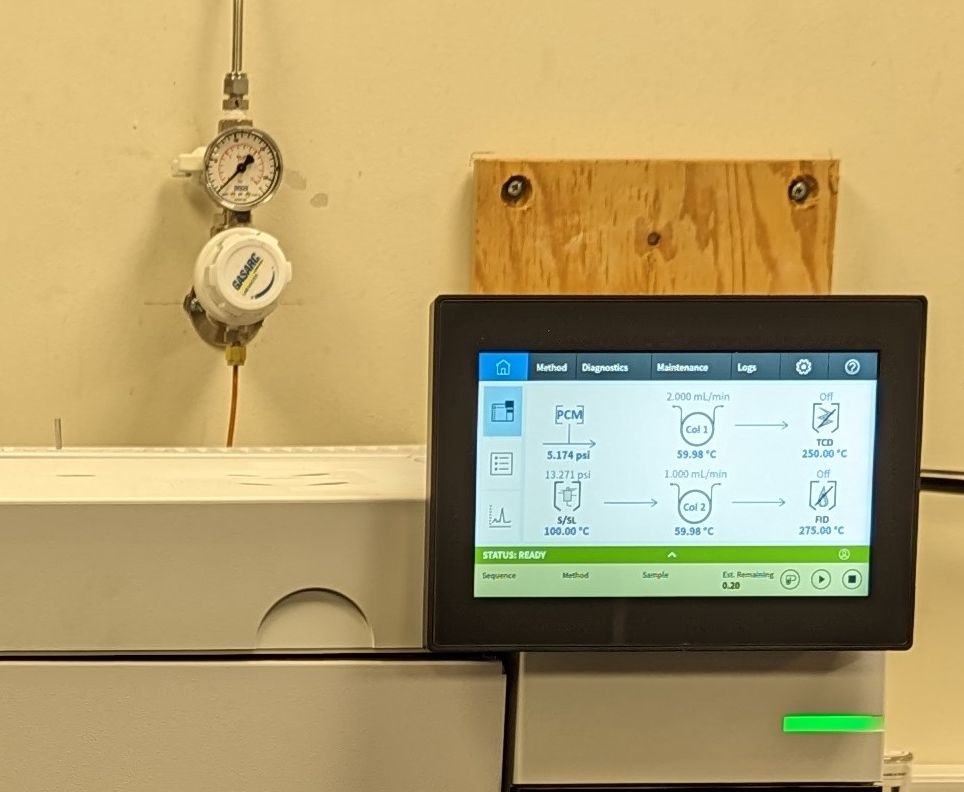
The sample is introduced into a heated inlet, often by injecting a solution or by use of a headspace sampler, where it is volatilised. It then passes along a column of material, typically 0.25mm in diameter and 25 metres long which is coiled in a heated oven. The effluent from this column is passed through the detector and the analyte detected by the change in an electrical signal generated by the FID - Flame Ionisation Detector.
Identification is achieved by measuring the time taken between injection and the compound being detected.
Unfortunately we are unable to provide quantitation if a reference material is not available. Occasionally it may be possible to use a closely related compound but this approach is likely to yield a result that is, at best, an approximation of the amount present otherwise relative concentrations can be measured between samples.
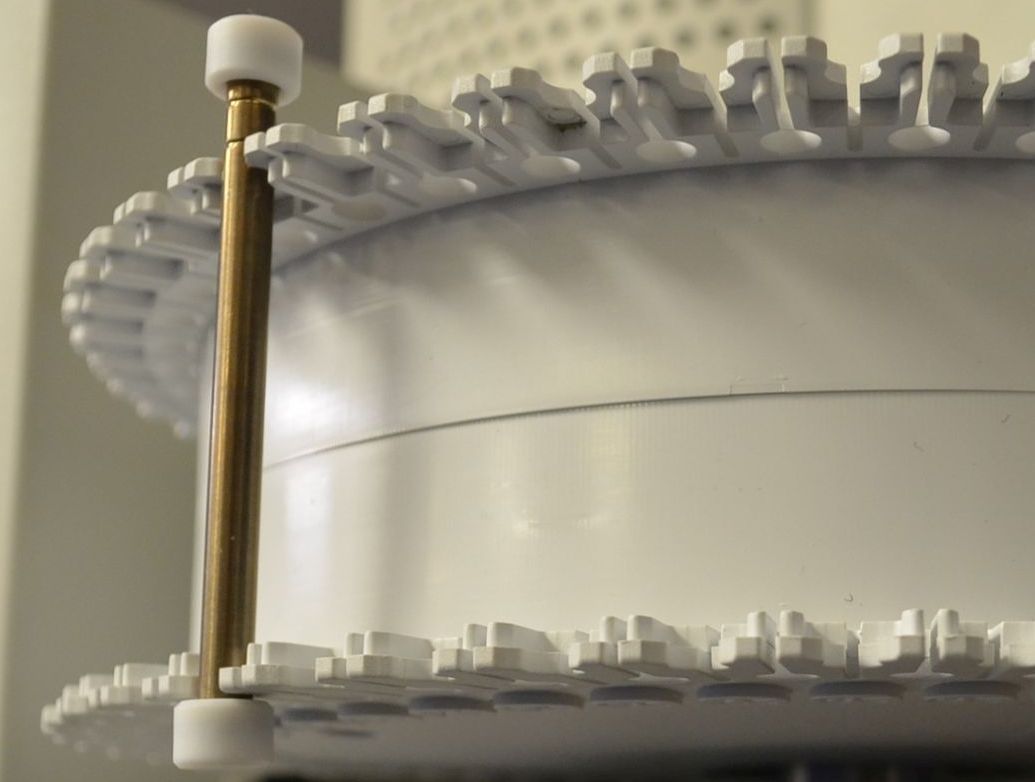
GC Columns
The heart of any GC system is the column. The majority of columns are now described as capillary columns which are generally between 15 and 100metres long with an internal diameter of 0.2 to 0.5mm. They are coiled on a cage to fit in the oven. LPD Lab Services have a wide ranging collection columns due to large number of bespoke analyses carried out. If your analysis requires a particular column we can obtain this.
The ability of columns to discriminate between closely related compounds continues to improve. Modern columns show a much greater resolution of compounds and can separate compounds according to the conformation of their carbon to carbon double bonds (i.e. cis and trans) and even chirality (i.e. “right handed” or “left handed“ configurations of the molecule).
An alternative type of column is the packed column. These are much bulkier than the modern capillary columns and the use of these is now comparatively rare but they are still requires for some legacy methods and we have an inlet which allows the connection of these columns.
Thermal Desorption GC Capability
A thermal desorption unit or a pyrolysis system can be attached for use with diffusive atmospheric sampling apparatus. The diffusive tubes are used for passive sampling of workplace atmospheres and can be worn on the lapel of operatives where they absorb a representative sample of the workplace atmospheric organics or samples can be collected using locally placed pumps with calibrated levels of air handling.
Application Notes
| Document Title | View |
| GC & XPS of Thermal processed Ni Cr & Catalytic Activity. |
Our site experts on GC are Kim Nickson, Matt Edwards and Aeryn May.
Please contact us to discuss how your requirements can be met using this or any of our analytical techniques. We can issue no-obligation quotations once we have discussed your needs and can offer two levels of service Priority and Standard. We also offer preferential rates for longer term analysis contracts.