Weld Assessment and Weld Failure Analysis
LPD Lab Services can perform weld assessment and weld failure analysis. The laboratory conducts metallurgical macroscopic and microscopic examination as well as hardness testing of steel and non-ferrous alloy welds and weld overlays, according to procedures such as BS EN 1321 and ISO 17639. By its nature this is a destructive method whereby one or more cross-sections are taken from the weldment. The section is metallographically prepared (ground, polished and etched) before being examined for defects. Weld assessment is typically performed for welder assessment when testing a welder’s ability to perform a specific weld procedure. Weld assessment is also performed during failure examination when a weld is suspected of being the cause of or a contributing factor to failure.
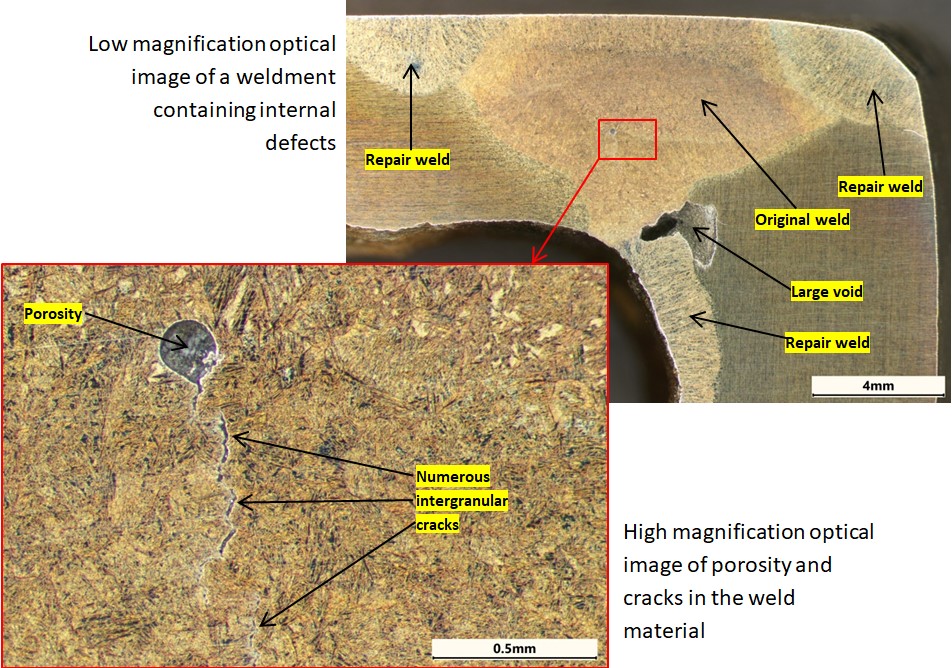
External or surface breaching weld defects can be detected visually, or with the aid of dye penetrant inspection. Internal defects are best detected by radiography or macro examination of cross sections. There are numerous weld defects that could cause failure, depending on the severity of the defect. Some of these are gas porosity, shrinkage porosity, non-metallic inclusions, undercut, lack of fusion, lack of penetration, insufficient weld size, precipitation of deleterious phases in the heat affected zone HAZ, cracks in the weld or heat affected zone.
 Typical causes of welding defects:
Typical causes of welding defects:
- Wrong filler material
- Contaminated welding rods or dirty weld surfaces
- Incorrect joint profile or edge preparation
- Neglecting to preheat where required
- Inappropriate shielding
- Inappropriate feed rate and/or weld speed
- Too high heat input
- Incorrect post weld heat treatment (PWHT).
Basic types of weld joints investigated:
- Butt joint
- Corner joint
- Edge joint
- Lap joint
- Tee joint.
Basic types of weld processes used and assessed:
- Arc welding, such as MIG, TIG and MMA.
- Gas welding, such as oxy-acetylene.
- Electric resistance welding, typically spot welding and seam welding.
- Solid state welding, such as friction welding and explosive welding.
- Laser beam welding.